Mandarin Orange Nutrition Facts A Comprehensive Guide
Comparison with Other Citrus Fruits: Mandarin Orange Nutrition Facts

Mandarin orange nutrition facts – Mandarin oranges, while sharing the citrus family with oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, possess a distinct nutritional profile and sensory experience. A comparative analysis reveals subtle yet significant differences in their vitamin and mineral content, impacting their overall contribution to a healthy diet. Understanding these variations allows for a more informed choice based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
The following table summarizes the nutritional differences between mandarin oranges and other common citrus fruits. Note that values can vary depending on factors such as growing conditions and ripeness.
Nutritional Comparison of Citrus Fruits
| Nutrient | Mandarin Orange (per 100g) | Orange (per 100g) | Grapefruit (per 100g) | Lemon (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (mg) | 40-50 | 50-60 | 40-50 | 50-60 |
| Fiber (g) | 1-2 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 |
| Potassium (mg) | 150-200 | 200-250 | 150-200 | 100-150 |
| Calories | 40-50 | 45-55 | 40-50 | 20-30 |
Note: These are approximate values and can vary based on the specific variety and growing conditions.
Mandarin oranges are a fantastic source of Vitamin C and fiber, offering a healthy and refreshing snack. However, if you’re looking for a less healthy, but perhaps more satisfying, alternative, you might want to check out the nutritional information for other foods, such as the in n out nutrition facts , before making a decision. Returning to mandarin oranges, their low calorie count makes them an excellent choice for those watching their weight, complementing a balanced diet.
Taste and Texture Differences
Mandarin oranges are generally known for their sweeter, less acidic taste compared to oranges and grapefruits. Their segments are easier to peel and separate, offering a convenient and enjoyable eating experience. Oranges, while also sweet, often have a more pronounced tartness. Grapefruits are significantly more tart and bitter, while lemons are overwhelmingly acidic and primarily used for juice or as a flavoring agent, rather than eaten whole.
The texture of mandarin oranges is typically softer and more delicate than that of oranges or grapefruits.
Unique Health Benefits of Mandarin Oranges, Mandarin orange nutrition facts
While all citrus fruits are excellent sources of Vitamin C and antioxidants, mandarin oranges stand out for their higher concentration of certain carotenoids, particularly beta-cryptoxanthin. Beta-cryptoxanthin is a precursor to vitamin A and has been linked to a reduced risk of certain cancers and improved eye health. Some studies suggest that mandarin oranges may also have unique anti-inflammatory properties compared to other citrus fruits, although further research is needed in this area.
The ease of consumption of mandarin oranges, due to their easy peeling and segmentation, might also contribute to higher overall consumption of this nutritious fruit, leading to greater health benefits.
Mandarin Oranges in a Balanced Diet
Mandarin oranges, with their delightful sweetness and abundance of vitamins and antioxidants, seamlessly integrate into a balanced and healthy diet. Their versatility allows for inclusion in various meal components, enhancing both nutritional value and flavor profiles. By understanding how to best incorporate them into our daily meals and selecting them wisely, we can fully leverage the benefits these little citrus gems offer.
Incorporating mandarin oranges into your daily meals is a simple yet effective way to boost your intake of essential vitamins and minerals. Their naturally sweet flavor makes them a delicious and refreshing addition to both sweet and savory dishes. A balanced diet should include a variety of fruits and vegetables, and mandarin oranges provide a valuable contribution to this goal.
They’re low in calories and high in fiber, making them a smart choice for weight management as well.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Mandarin Oranges
The following meal plan demonstrates how easily mandarin oranges can be incorporated into a balanced daily diet, offering a variety of flavor combinations and nutritional benefits. Remember that portion sizes should be adjusted based on individual needs and caloric goals.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with a handful of chopped mandarin oranges, a sprinkle of chia seeds, and a drizzle of honey.
- Lunch: A mixed green salad with grilled chicken or fish, mandarin orange segments, crumbled feta cheese, and a light vinaigrette dressing.
- Dinner: Roasted salmon with a side of quinoa and steamed asparagus, garnished with mandarin orange slices for a touch of sweetness and acidity.
Incorporating Mandarin Oranges into Recipes
Mandarin oranges offer a unique flavor profile that complements both sweet and savory dishes. Their versatility extends beyond simple snacking, enhancing the taste and nutritional value of a wide array of recipes.
- Salads: Add mandarin orange segments to salads for a burst of sweetness and vitamin C. They pair well with greens, nuts, and cheeses.
- Desserts: Incorporate mandarin oranges into muffins, cakes, or fruit crumbles. Their juice can also be used to create glazes or sauces.
- Main Courses: Mandarin oranges can add a surprising yet delightful twist to savory dishes. Consider using them in stir-fries, alongside pork or chicken, or as a garnish for fish dishes.
Selecting and Storing Mandarin Oranges
Proper selection and storage are crucial for maintaining the freshness and nutritional value of mandarin oranges. Choosing ripe and properly stored fruits ensures you maximize their flavor and health benefits.
- Selection: Choose mandarin oranges that are firm to the touch, with smooth, unblemished skin. Avoid those that feel soft or have bruises or blemishes.
- Storage: Store mandarin oranges at room temperature for a few days. For longer storage, refrigerate them in a plastic bag to maintain their freshness for up to a week. Avoid washing them until just before consumption to prevent premature spoilage.
Potential Allergic Reactions and Considerations
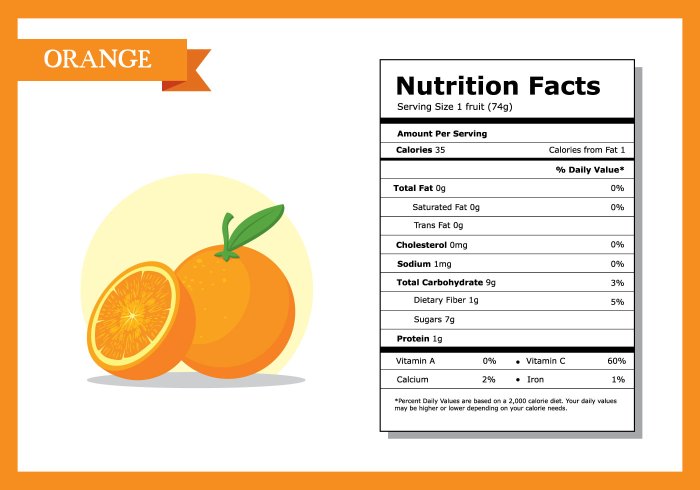
Mandarin oranges, while generally safe and nutritious, can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. These reactions range from mild to severe, highlighting the importance of understanding potential risks and taking appropriate precautions. The severity of an allergic reaction depends on factors such as the amount of mandarin orange consumed, the individual’s sensitivity, and the presence of other allergens.Allergic reactions to mandarin oranges are primarily caused by proteins found within the fruit.
These proteins can trigger an immune response in sensitive individuals, leading to a range of symptoms. While cross-reactivity with other citrus fruits is common, the specific allergens and their impact can vary.
Allergic Reaction Symptoms
Symptoms of a mandarin orange allergy can manifest in various ways, from mild skin reactions to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis. Mild reactions might include itching or tingling in the mouth, hives (urticaria), or eczema. More severe reactions can involve swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), difficulty breathing, and a drop in blood pressure (anaphylaxis). In cases of anaphylaxis, immediate medical attention is crucial.
The speed of onset and severity of symptoms can differ significantly between individuals. For example, some individuals might experience a mild rash after eating a small amount of mandarin orange, while others could experience a severe reaction after even minimal contact.
Medication Interactions
While not extensively documented, there’s a possibility of interaction between mandarin oranges and certain medications. The high vitamin K content in mandarin oranges might affect individuals taking anticoagulant medications like warfarin, potentially impacting blood clotting. Furthermore, the high citric acid content could interact with certain medications, affecting their absorption or efficacy. It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you are taking medication and have concerns about consuming mandarin oranges.
This is particularly important for individuals on medications that are known to interact with foods containing high levels of vitamins or acids. For example, individuals taking medication to lower blood pressure might need to monitor their intake of potassium-rich foods like mandarin oranges, as excessive potassium can interfere with the medication’s effectiveness.
Precautions for Individuals with Dietary Restrictions
Individuals with specific dietary restrictions should exercise caution when consuming mandarin oranges.
- Individuals with citrus allergies: Those with known allergies to other citrus fruits should proceed with caution, as cross-reactivity is possible. A small test amount is recommended initially, followed by careful observation for any adverse reactions.
- Individuals with gastrointestinal issues: The high acidity of mandarin oranges may exacerbate symptoms in individuals with conditions like acid reflux or gastritis. Consumption should be moderated or avoided entirely if symptoms worsen.
- Individuals with diabetes: Mandarin oranges contain natural sugars, so individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels carefully after consumption and adjust their medication or insulin dosage as needed.
- Individuals on medication: As mentioned previously, individuals taking certain medications, particularly anticoagulants or those affecting blood pressure or potassium levels, should consult their doctor before significantly increasing their mandarin orange consumption.
FAQs
Are mandarin oranges good for weight loss?
Mandarins are relatively low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to feelings of fullness and aid in weight management as part of a balanced diet and exercise plan. However, they are not a miracle weight-loss food.
Can I eat mandarin oranges if I have diabetes?
While mandarins contain natural sugars, their glycemic index is relatively low compared to some other fruits. However, individuals with diabetes should still monitor their blood sugar levels and consume them in moderation as part of a balanced meal plan, consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
How long can I store mandarin oranges?
Mandarin oranges should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain freshness. They typically last for about a week, though this can vary depending on their ripeness when purchased.
Are mandarin oranges acidic?
Yes, mandarin oranges are slightly acidic, similar to other citrus fruits. Individuals with sensitive stomachs might experience some discomfort if consumed in large quantities.
What are the best ways to prepare mandarin oranges?
Mandarin oranges can be enjoyed fresh, added to salads, incorporated into yogurt parfaits, or used as a topping for oatmeal or other breakfast dishes. They can also be juiced or used in various desserts and sauces.
